
India, home to one of the world’s largest youth populations, is on the verge of a significant economic transformation. The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE) plays a key role in this transformation by shaping the nation’s skill development ecosystem. Through its numerous initiatives, MSDE aims to bridge the skill gap, make the youth job-ready, and foster a culture of entrepreneurship, positioning India to meet global demands.
Why is skill development crucial for India?
India boasts the world’s largest youth demographic, with 65% of its population under the age of 35. This youth bulge offers a tremendous opportunity for economic growth. However, a major challenge lies in the gap between the skills that industries require and the abilities of the existing india’s workforce. The MSDE, through a series of focused initiatives, seeks to bridge this gap by providing quality, industry-relevant training and creating employment opportunities, ultimately preparing India for the challenges of the future.
Key initiatives by the MSDE
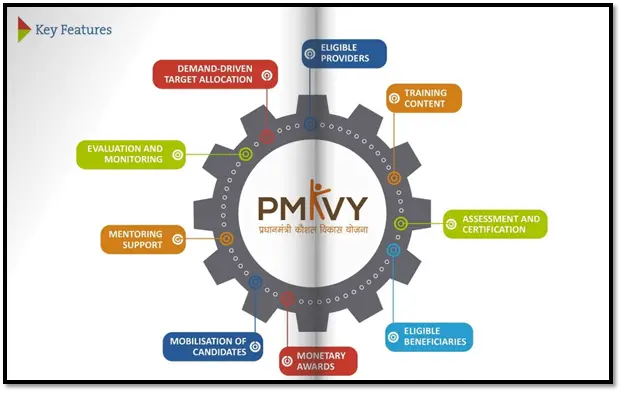
1. Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY)
The Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY), launched in 2015, is MSDE’s flagship program. It aims to provide skill training to the youth across various sectors. So far, more than 14.2 million individuals have been trained through PMKVY. The program has recently pivoted towards skilling individuals in cutting-edge fields such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), Internet of Things (IoT), Big Data, and Robotics, aligning with the demands of Industry 4.0.
In addition to providing urban youth with training, PMKVY has also reached rural and underprivileged communities, ensuring equitable access to skill development opportunities. By 2024, PMKVY had achieved a remarkable 52.3% female participation rate, showcasing its success in encouraging women to participate in the workforce. In the future, the program is set to expand its reach, targeting backward regions and strengthening vocational training programs.
2. Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS)
The Craftsmen Training Scheme (CTS), which dates back to 1950, is one of India’s most established vocational training initiatives. It operates through a network of over 14,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs), offering training in 150+ trades, ranging from traditional skills like electrician, fitter, and welder to modern fields such as information technology, fashion design, and automobile engineering.
CTS has recently incorporated advanced simulators, smart classrooms, and a data-driven ITI grading system to ensure the quality of training and its relevance to industry requirements. The government aims to modernize and upgrade more than 1,000 ITIs by 2024, making them equipped to meet contemporary demands.
3. National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS)
The National Apprenticeship Promotion Scheme (NAPS) is crucial in bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills by offering real-time, on-the-job training in industries. Since its launch, over 3.2 million apprentices have gained valuable experience. The scheme incentivizes industries to hire apprentices by offering financial subsidies.
In 2023, NAPS introduced the Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) system for stipend payments, ensuring a transparent and efficient payment mechanism for apprentices. With a target to increase apprenticeship enrolment by 25% by 2025, the program aims to boost participation across sectors like manufacturing, healthcare, and information technology.
4. Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS)
Jan Shikshan Sansthan (JSS) is focused on providing skill development opportunities to non-literate and semi-literate individuals, particularly in rural and economically backward regions. With an impressive 82% of the beneficiaries being women, JSS plays a significant role in empowering women from marginalized communities. By 2024, JSS had trained 2.6 million people in skills such as handicrafts, tailoring, and basic IT, fostering self-employment and entrepreneurship in rural areas.
By promoting traditional crafts and local arts, JSS not only ensures employability but also helps preserve India’s cultural heritage. MSDE has plans to set up 100 additional JSS centers by 2025, further expanding its outreach.
5. National Institute for Entrepreneurship and Small Business Development (NIESBUD)
Recognizing the importance of entrepreneurship in economic growth, the MSDE, through NIESBUD, has been actively promoting entrepreneurial culture across the country. NIESBUD provides specialized training in areas such as financial management, marketing, and business strategy, having trained over 321,000 budding entrepreneurs so far. These initiatives aim to transform job seekers into job creators, resonating with the government’s Atmanirbhar Bharat vision.
MSDE’s recent launch of the Skill India Entrepreneurial Hub is a step towards nurturing entrepreneurship by providing mentorship, incubation services, and financial support to aspiring entrepreneurs, with a particular focus on sectors like technology and agriculture.
Driving technological innovation in skill development
In 2024, the MSDE unveiled the Skill India Digital Hub, an integrated platform that brings together skill training, job matching, and certification services. Leveraging advanced technologies like AI and Big Data Analytics, this platform tailors training programs based on industry trends and gaps. It also connects job seekers with employers in real time, ensuring that individuals who complete skill training programs can quickly find relevant employment.
Moreover, India’s government has established International Skill Development Centers (ISDCs) to train the workforce to global standards, focusing on industries such as construction, healthcare, and IT. These centers aim to equip the Indian youth with the skills needed to access employment opportunities not just in India but also in international markets.
Boost to skill development in the union budget 2024-25
In the 2024-25 Union Budget, the Indian government made a significant allocation of ₹4,000 crores to skill development programs, reaffirming its commitment to creating a future-ready workforce. The government also launched a new centrally sponsored scheme aimed at skilling 2 million youth in emerging technologies such as AI, automation, and data science over the next five years. Furthermore, initiatives are in place to revitalize 1,000 ITIs and expand apprenticeship programs, aligning skill development efforts with the future needs of the economy.
Conclusion: Towards a skilled and self-reliant India
The Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship is playing a pivotal role in equipping India’s workforce for the present and the future. By focusing on skill development, promoting entrepreneurship, and embracing technological advancements, the ministry is ensuring that India’s young population is ready to seize opportunities in both domestic and global markets. These initiatives lay the foundation for India’s emergence as a $5 trillion economy, driving growth, innovation, and self-reliance.
भारत के कार्यबल को सशक्त बनाना: कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता मंत्रालय की भूमिका
भारत, जो दुनिया की सबसे बड़ी युवा आबादी का घर है, एक महत्वपूर्ण आर्थिक परिवर्तन के कगार पर है। कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता मंत्रालय (MSDE) इस परिवर्तन में एक प्रमुख भूमिका निभा रहा है। मंत्रालय के विभिन्न कार्यक्रमों के माध्यम से, कौशल अंतर को पाटने, युवाओं को नौकरी के लिए तैयार करने और उद्यमिता की संस्कृति को बढ़ावा देने के लिए काम किया जा रहा है, जिससे भारत को वैश्विक मांगों के अनुरूप तैयार किया जा सके।
कौशल विकास भारत के लिए क्यों महत्वपूर्ण है?
भारत की जनसंख्या का 65% हिस्सा 35 वर्ष से कम उम्र का है। यह युवा आबादी भारत को आर्थिक विकास के लिए एक अनूठा अवसर प्रदान करती है। हालांकि, नियोक्ताओं की आवश्यकताओं और मौजूदा कार्यबल की क्षमताओं के बीच एक महत्वपूर्ण अंतर है। कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता मंत्रालय (MSDE) विभिन्न योजनाओं के माध्यम से इस अंतर को पाटने के लिए प्रयासरत है, जिससे युवा उद्योग-उन्मुख कौशल प्राप्त करें और रोजगार के बेहतर अवसर प्राप्त कर सकें।
MSDE की प्रमुख पहलें
1. प्रधानमंत्री कौशल विकास योजना (PMKVY)
प्रधानमंत्री कौशल विकास योजना (PMKVY), जो 2015 में शुरू हुई, MSDE की प्रमुख योजना है। इसका उद्देश्य विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में युवाओं को कौशल प्रशिक्षण प्रदान करना है। अब तक 1.42 करोड़ से अधिक लोग इस योजना के तहत प्रशिक्षित हो चुके हैं। हाल के वर्षों में, PMKVY ने कौशल विकास को बढ़ावा देने के लिए कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता (AI), इंटरनेट ऑफ थिंग्स (IoT), बिग डेटा, और रोबोटिक्स जैसे क्षेत्रों पर ध्यान केंद्रित किया है, जो इंडस्ट्री 4.0 की मांगों के अनुरूप है।
PMKVY ने ग्रामीण और हाशिए के समुदायों में भी अपनी पहुंच सुनिश्चित की है, जिससे सभी को कौशल विकास के समान अवसर मिल सकें। 2024 तक, इस योजना में 52.3% महिला भागीदारी दर्ज की गई, जो महिलाओं को कार्यबल में शामिल करने के प्रयासों की सफलता को दर्शाता है। आने वाले वर्षों में, योजना का विस्तार करते हुए पिछड़े क्षेत्रों में विशेष प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रम शुरू किए जाएंगे।
2. क्राफ्ट्समेन ट्रेनिंग स्कीम (CTS)
क्राफ्ट्समेन ट्रेनिंग स्कीम (CTS), जिसे 1950 में शुरू किया गया था, भारत की सबसे पुरानी और व्यापक व्यावसायिक प्रशिक्षण योजनाओं में से एक है। यह योजना 14,000 से अधिक औद्योगिक प्रशिक्षण संस्थानों (ITIs) के माध्यम से संचालित होती है, जो 150+ ट्रेड्स में प्रशिक्षण प्रदान करती है। इनमें इलेक्ट्रीशियन, फिट्टर, वेल्डर जैसे पारंपरिक क्षेत्रों के साथ-साथ सूचना प्रौद्योगिकी, फैशन डिजाइन और ऑटोमोबाइल इंजीनियरिंग जैसे आधुनिक क्षेत्र भी शामिल हैं।
हाल के वर्षों में CTS ने स्मार्ट क्लासरूम्स, एडवांस्ड सिम्युलेटर्स, और ITI ग्रेडिंग सिस्टम जैसे नवीनतम तकनीकों को अपनाया है, ताकि प्रशिक्षण की गुणवत्ता और उद्योग की आवश्यकताओं के अनुरूप हो सके। सरकार ने 2024 तक 1,000 से अधिक ITIs को आधुनिक बनाने का लक्ष्य रखा है, ताकि वे समकालीन मांगों को पूरा कर सकें।
3. राष्ट्रीय शिक्षुता प्रोत्साहन योजना (NAPS)
राष्ट्रीय शिक्षुता प्रोत्साहन योजना (NAPS) उद्योगों में वास्तविक समय में, व्यावहारिक अनुभव प्रदान करते हुए सैद्धांतिक और व्यावहारिक ज्ञान के बीच की खाई को पाटने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाती है। इस योजना के तहत 32 लाख से अधिक शिक्षु लाभान्वित हो चुके हैं। NAPS उद्योगों को शिक्षुओं को नियुक्त करने के लिए वित्तीय सब्सिडी भी प्रदान करती है।
2023 में, NAPS ने डायरेक्ट बेनिफिट ट्रांसफर (DBT) प्रणाली शुरू की, जिससे शिक्षुओं को स्टाइपेंड का भुगतान पारदर्शी और समय पर हो सके। 2025 तक योजना का लक्ष्य शिक्षुता नामांकन को 25% तक बढ़ाना है, जिसमें निर्माण, स्वास्थ्य सेवा, और सूचना प्रौद्योगिकी जैसे क्षेत्रों पर विशेष ध्यान दिया जाएगा।
4. जन शिक्षण संस्थान (JSS)
जन शिक्षण संस्थान (JSS) का मुख्य उद्देश्य ग्रामीण और आर्थिक रूप से पिछड़े क्षेत्रों के अशिक्षित और अर्ध-शिक्षित लोगों को कौशल प्रशिक्षण प्रदान करना है। JSS के अंतर्गत 82% से अधिक लाभार्थी महिलाएँ हैं, जिससे यह महिलाओं के सशक्तिकरण में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है। 2024 तक, JSS ने 26 लाख लोगों को विभिन्न कौशलों जैसे हस्तशिल्प, सिलाई, और बुनियादी आईटी में प्रशिक्षित किया है, जिससे वे आत्मनिर्भर हो सकें और उद्यमिता की दिशा में कदम बढ़ा सकें।
JSS के माध्यम से पारंपरिक शिल्प और स्थानीय कलाओं को प्रोत्साहित किया जाता है, जो न केवल रोजगार के अवसर प्रदान करते हैं, बल्कि भारत की सांस्कृतिक धरोहर को भी बनाए रखते हैं। 2025 तक, सरकार ने 100 नए JSS केंद्र खोलने की योजना बनाई है ताकि इसकी पहुँच और अधिक क्षेत्रों तक हो सके।
5. राष्ट्रीय उद्यमिता और लघु व्यवसाय विकास संस्थान (NIESBUD)
MSDE के तहत राष्ट्रीय उद्यमिता और लघु व्यवसाय विकास संस्थान (NIESBUD) उद्यमशीलता को बढ़ावा देने में सक्रिय भूमिका निभा रहा है। यह संस्थान वित्तीय प्रबंधन, विपणन और व्यावसायिक रणनीति जैसे क्षेत्रों में विशेष प्रशिक्षण प्रदान करता है। 3.21 लाख से अधिक नवोदित उद्यमियों को अब तक NIESBUD द्वारा प्रशिक्षित किया जा चुका है। इस पहल का उद्देश्य नौकरी चाहने वालों को नौकरी सृजक बनने के लिए प्रेरित करना है, जो आत्मनिर्भर भारत के दृष्टिकोण से मेल खाता है।
MSDE ने हाल ही में कौशल भारत उद्यमिता हब लॉन्च किया है, जिसका उद्देश्य उद्यमियों को सलाह, प्रशिक्षण, और वित्तीय सहायता प्रदान करना है। यह हब विशेष रूप से प्रौद्योगिकी और कृषि क्षेत्रों में नवाचार को बढ़ावा देगा।
तकनीकी नवाचार और कौशल विकास
2024 में, MSDE ने कौशल भारत डिजिटल हब लॉन्च किया, जो एकीकृत प्लेटफ़ॉर्म है जिसमें कौशल प्रशिक्षण, नौकरी मिलान, और प्रमाणन सेवाएँ शामिल हैं। इस हब में कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता (AI) और बिग डेटा एनालिटिक्स जैसी प्रौद्योगिकियों का उपयोग किया गया है, जिससे प्रशिक्षण कार्यक्रम उद्योग की मांगों के अनुसार तैयार किए जाते हैं। यह हब प्रशिक्षित युवाओं को नियोक्ताओं से जोड़ने में मदद करता है।
इसके अलावा, अंतरराष्ट्रीय कौशल विकास केंद्रों (ISDCs) की स्थापना भी की गई है, जिनका उद्देश्य भारतीय युवाओं को वैश्विक मानकों के अनुसार प्रशिक्षित करना है। इस पहल के अंतर्गत, निर्माण, स्वास्थ्य सेवा, और आईटी जैसे क्षेत्रों में कौशल विकास किया जा रहा है, ताकि भारतीय युवाओं को अंतर्राष्ट्रीय स्तर पर भी रोजगार के अवसर मिल सकें।
2024-25 के केंद्रीय बजट में कौशल विकास को बढ़ावा
2024-25 के केंद्रीय बजट में, कौशल विकास कार्यक्रमों के लिए ₹4,000 करोड़ का आवंटन किया गया है, जो सरकार की ओर से भविष्य के लिए तैयार कार्यबल बनाने की प्रतिबद्धता को दर्शाता है। इसके तहत, सरकार ने एक नई योजना शुरू की है, जिसका उद्देश्य अगले पांच वर्षों में 20 लाख युवाओं को कृत्रिम बुद्धिमत्ता, ऑटोमेशन, और डेटा साइंस जैसी उभरती प्रौद्योगिकियों में प्रशिक्षित करना है। साथ ही, 1,000 ITIs को आधुनिक बनाने और प्रशिक्षुता कार्यक्रमों के विस्तार की पहल की जा रही है।
निष्कर्ष: एक कुशल और आत्मनिर्भर भारत की दिशा में
कौशल विकास और उद्यमिता मंत्रालय (MSDE) भारत के कार्यबल को वर्तमान और भविष्य के लिए तैयार करने में महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभा रहा है। कौशल विकास, उद्यमिता को बढ़ावा देने, और तकनीकी उन्नति को अपनाने पर ध्यान केंद्रित करके, मंत्रालय यह सुनिश्चित कर रहा है कि भारत की युवा आबादी घरेलू और वैश्विक दोनों बाजारों में अवसरों का लाभ उठा सके। ये पहलें भारत को $5 ट्रिलियन की अर्थव्यवस्था बनने की दिशा में मजबूत नींव प्रदान कर रही हैं, जिससे विकास, नवाचार, और आत्मनिर्भरता को बढ़ावा मिलेगा।










Very informative